TestCafe JS SDK
The Evinced TestCafe JS SDK integrates with new or existing TestCafe tests to automatically detect accessibility issues. By adding a few lines of code to your TestCafe project, you can begin analyzing all the web pages and DOM changes to provide a dynamic view of how your site can become more accessible. As a result of the test, a rich and comprehensive report is generated to easily track issues to resolution.
Interested in seeing this in action? Contact us to get started!
Prerequisites
- TestCafe version 3.6.0 or higher
Get started
Installation
To install TestCafe JS SDK you will need either a file provided by Evinced Support or access to a remote repository that provides it. If you have neither, contact us to get started.
Installation with a locally provided file
With a local copy of the TestCafe JS SDK gzipped tar package (.tgz extension), install it in your project using NPM or Node package manager of your choice:
1# Using NPM2npm install -D <path to js-testcafe-sdk-<version>.tgz file>
Installation from a remote repository
Evinced Customers have the option of accessing TestCafe JS SDK from a remote repository — the Evinced Jfrog Artifactory — to keep their SDK version up-to-date and to share the SDK internally at their organization.
When access is enabled, TestCafe JS SDK is available at
https://evinced.jfrog.io/artifactory/restricted-npm/%40evinced/js-testcafe-sdk.
Installation using NPM:
1npm install @evinced/js-testcafe-sdk
Authentication
To launch TestCafe JS SDK, you need to have a Service ID and an API Key.
Where to find your Evinced SDK credentials
These credentials are available via the Evinced Product Hub in the “Automation for Web” or “Automation for Mobile” product areas. Click the “Get SDK” button to see the Service Account ID and API Key at the bottom of the page.
Authenticate for Offline Testing
There are two methods to provide the token: online mode and offline mode. Online mode contacts the Evinced Licensing Server. Offline mode assumes that an Evinced employee has supplied a JSON Web Token (JWT). If an offline token is required, please reach out to your account team or support@evinced.com.
Please set credentials in environment variables and reference the environment variables in code.
1# Offline mode2export EVINCED_SERVICE_ID=<serviceId>3export EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN=<token>45# Online mode6export EVINCED_SERVICE_ID=<serviceId>7export EVINCED_API_KEY=<apiKey>
Setting credentials, an example:
1// Online credentials2const { setCredentials } = require('@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk');34await setCredentials({5 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,6 secret: process.env.EVINCED_API_KEY7});89// OR1011// Offline credentials12const { setOfflineCredentials } = require('@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk');1314setOfflineCredentials({15 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,16 token: process.env.EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN,17});
Your First Test
SDK Initialization
To use TestCafe JS SDK, you first need to authenticate. Please refer to Authentication for details.
There is no any other specific initialization of SDK.
Add Evinced Accessibility Checks (Single Run Mode)
This is a simple example of how to add an Evinced accessibility scan to a test. Please note the inline comments that give detail on each test step.
1import { fixture } from "testcafe";2import { EvincedSDK } from "@evinced/testcafe-sdk";34fixture('Demo page')5 .page('https://demo.evinced.com/')67test('Demo page. evAnalyze', async t => {8 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);910 const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze();11 await t.expect(issues.length).eql(6);12});
Add Evinced Accessibility Checks (Continuous Mode)
This is an example of how to add a continuous Evinced accessibility scan to a test. Using the
evStart() and evStop() methods, the Evinced engine will continually scan in the background capturing all DOM changes and page navigation as the test is executed. This will capture all accessibility issues as clicking on drop-downs or similar interactions reveals more of the page. The advantage of continuous mode is that no interaction with the actual test code is needed.
1import { fixture } from "testcafe";2import { EvincedSDK } from "@evinced/testcafe-sdk";34fixture('Demo page')5 .page('https://demo.evinced.com/')67test('Continous mode for a static page', async t => {8 // Start the Evinced engine9 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);10 await evinced.evStart();1112 await t13 .click(homePage.typeDropdown)14 .click(homePage.tinyHomeOption)15 .click(homePage.whereDropdown)16 .click(homePage.eastCoastOption)17 .click(homePage.searchButton)18 .expect(secondPage.pageHeader.innerText).match(/Results for: Tiny House in East Coast/);1920 // Conclude the scan and store the issues found21 const foundIssues = await evinced.evStop();2223 // Assert that no accessbility issues were found24 await t.expect(foundIssues.length).eql(0);25});
API
EvincedSDK
Prepares the Evinced object for use in the project.
The specific SDK initialization is not needed. You need just import EvincedSDK in your test files.
1const { EvincedSDK } = require('@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk');
Refer to Configuration to see examples of initializing with options.
evAnalyze(options)
Scans the current page and returns a list of accessibility issues. This is the recommended method for static page analysis.
Note: This method is not supported if evStart() is already running.
1fixture('evAnalyze example')2 .page('https://demo.evinced.com/')34test('evAnalyze', async t => {5 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);67 const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze();8 await t.expect(issues.length).eql(6);9});
Returns Promise<Issue[]>.
The returned report object contains a list of accessibility issues.
For more information regarding reports as well as the report object itself, please refer to our detailed Web Reports page.
evStart(options)
Continually watches for DOM mutations and page navigation, recording accessibility issues
until the evStop() method is called. This method is recommended for dynamic page flows.
1fixture('evStart example')2 .page('https://demo.evinced.com/')34test('evStart-evStop', async t => {5 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);67 await evinced.evStart();8 const issues = await evinced.evStop();9 await t.expect(issues.length).eql(6);10});
Returns Promise<void>.
evStop(options)
Stops the issue-gathering process started by evStart().
1fixture('evStart example')2 .page('https://demo.evinced.com/')34test('evStart-evStop', async t => {5 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);67 await evinced.evStart();8 const issues = await evinced.evStop();9 await t.expect(issues.length).eql(6);10});
Returns Promise<Issue[]>.
The returned report object includes all accessibility issues detected between
the evStart() and evStop() method calls.
For more information regarding reports as well as the report object itself, please refer to our detailed Web Reports page.
evSaveFile(issues, format, destination)
Saves issues in a file with the specified format and location.
Supported formats are json, html, sarif, and csv.
Find detailed information in the Web Reports page.
1fixture('evSaveFile tests')2 .page('https://demo.evinced.com')34test('using evAnalyze', async t => {5 const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);67 const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze();8 await evinced.evSaveFile(issues, 'html', 'evincedTest.html');9 await evinced.evSaveFile(issues, 'json', 'evincedTest.json');10 await evinced.evSaveFile(issues, 'csv', 'evincedTest.csv');11 await evinced.evSaveFile(issues, 'sarif', 'evincedTest.sarif.json');12});
Returns Promise<void>.
Configuration
The same configuration object can be used when initializing the Evinced object
using evConfig.json and when calling the evStart()
and evAnalyze() methods but with a bit different consequences.
Providing options when initializing defines a global configuration for all calls
of evAnalyze() and evStart(), while providing options to
either of those methods affect only the test in which they are called.
Options provided in either evAnalyze() or evStart() override
those set in Evinced engine initialization.
Engines Configuration
Evinced uses two separate engines when scanning for accessibility issues, one is the aXe engine and the other is the Evinced engine. By default, Evinced disables the aXe Needs Review and Best Practices issues based on customer request and due to the fact they are mostly false positives. Please note this setting when comparing issue counts directly. See an example of how to enable Needs Review and Best practices issues in the Toggles section.
Configuration Object
To define global configuration for TestCafe JS SDK please use file evConfig.json in a root directory of your project.
1export type EvInitOptions = {2 rootSelector?: string;3 enableScreenshots?: boolean;4 axeConfig?: axe.RunOptions;5 skipValidations?: SkipValidation[];6 logging?: {7 LOGGING_LEVEL: string;8 ADD_LOGGING_CONTEXT?: boolean;9 };10 toggles?: { [key: string]: boolean };11};
Root Selector
Sets a CSS selector to limit the Evinced Engine to scan only the selected element and its children. Must be a valid CSS selector. If not set, the Evinced Engine will scan the entire document.
Default: no value
1const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);2await evinced.evStart({3 rootSelector: '.some-selector',4});5const issues = await evinced.evStop();
Axe Configuration
Configures Axe open-source accessibility toolkit, which the Evinced engine includes with its own, more extensive accessibility detection. For full Axe config options, see Axe Core API.
1const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);2const axeConfig = {3 rules: {4 "link-name": { enabled: false },5 },6};7const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze({8 initOptions: {9 axeConfig10 }11});
Engine Logging
Set level of messages the Evinced engine will print to the console.
Valid levels are "debug", "info", "warn" and "error".
Default: "error"
1const evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);2const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze({3 initOptions: {4 logging: {5 LOGGING_LEVEL: 'debug',6 ADD_LOGGING_CONTEXT: true,7 },8 }9});
Reports Screenshots
When true, the Evinced SDK will include screenshots in its reports that
highlight elements with accessibility issues.
Default: false.
Note: Enabling screenshots may affect test run performance.
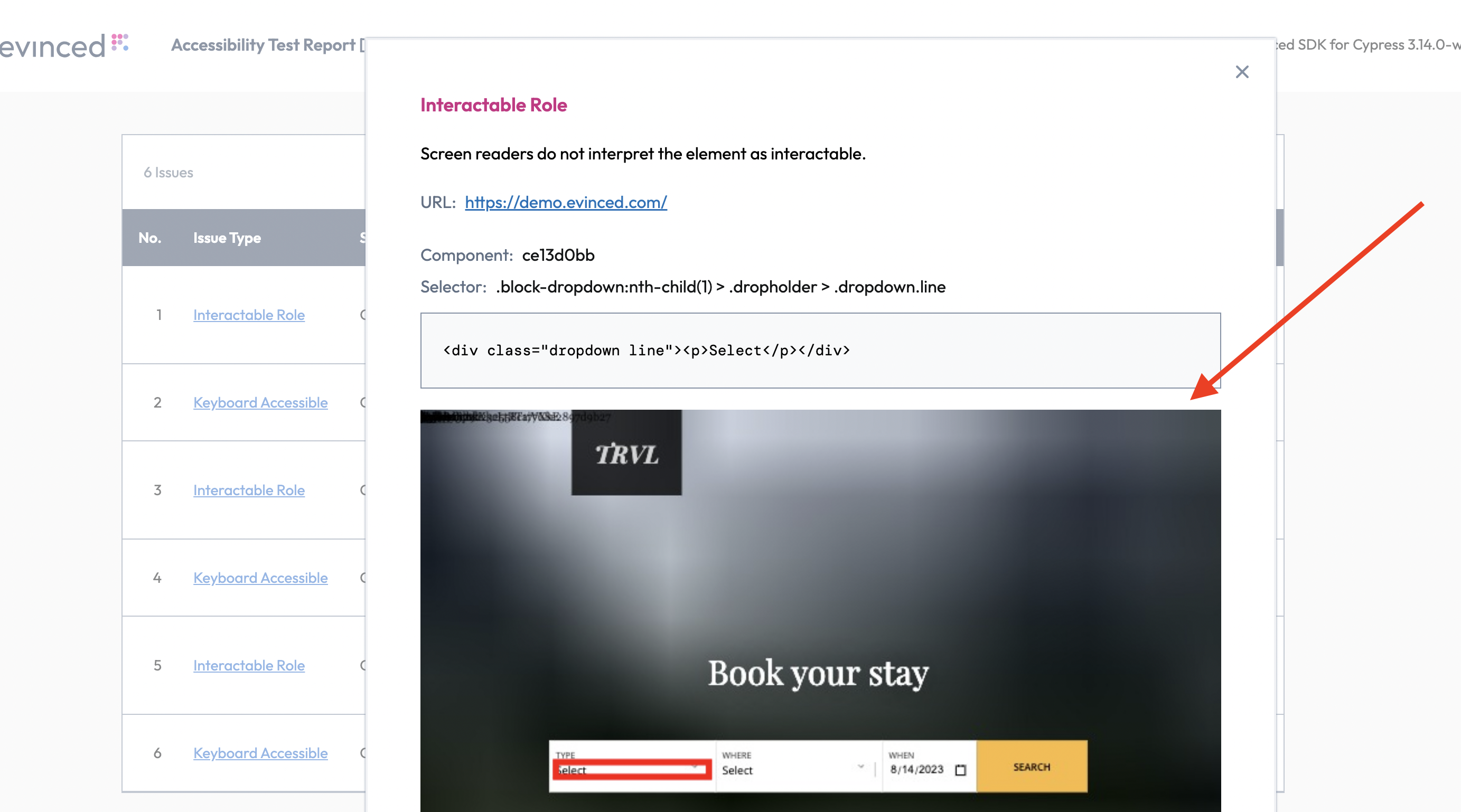
1const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze({2 initOptions: {3 enableScreenshots: true4 }5});
Toggles
Enables experimental features. Feature names and values may vary from release to release.
Example:
1const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze({2 initOptions: {3 toggles: {4 USE_AXE_NEEDS_REVIEW: true,5 USE_AXE_BEST_PRACTICES: true6 }7 }8});
Skip Validations
Sets validation types to be skipped for specified URL pattern and CSS selector. Issue type IDs can be found by inspecting a JSON report as described in Web Reports.
Default: no validations skipped.
1const skipSelector = {2 selector: 'testValue.slds-checkbox',3 urlRegex: '.*',4 validationTypes: ["WRONG_SEMANTIC_ROLE", "NOT_FOCUSABLE", "NO_DESCRIPTIVE_TEXT"],5};6await evinced.evStart({ skipValidations: [skipSelector] });
Recording Service
This setting controls how frequently event-triggered functions are executed, helping to optimize performance and responsiveness. The option does not enable or disable the event-handling service itself but determines how frequently events are processed based on the selected mode.
Available modes:
debounce– Delays execution until a set time has passed since the last event. Useful for actions triggered by continuous input, such as typing in a search box, to avoid excessive function calls.throttle– Ensures execution at fixed intervals, regardless of event frequency. Ideal for scenarios like handling window resize events or scroll tracking, where limiting execution prevents performance degradation.
Default: Functions execute as triggering events occur.
An example of how to modify settings:
1const evincedService = new EvincedSDK(t);23await evincedService.evStart({4 recordingService: {5 ENABLE_DEBOUNCE_NEW_SELECTORS: true,6 DEBOUNCE_NEW_SELECTORS_MS: 500,7 DELAY_MODE: 'throttle'8 },9});1011await t.navigateTo('https://demo.evinced.com/')1213await evincedService.evStop();
Shadow DOM Support
Shadow DOM is now supported by default. No additional configuration is needed.
Proxy
Configures proxy server access settings. Needed to enable outbound communication to the Evinced Platform through a proxy server.
In TestCafe, you can configure proxy settings via environment variables. These settings allow you to specify the proxy URL, as well as optional username and password for authentication with the proxy server. The SDK supports both HTTP and HTTPS proxies.
Global Proxy Configuration:
You can configure the proxy globally by setting the environment variables for HTTP or HTTPS proxies. The SDK will automatically apply the proxy settings when attempting to upload issues to the Evinced Platform.
HTTP_PROXY for HTTP connections
HTTPS_PROXY for HTTPS connections
Additionally, you can provide credentials for proxy authentication via the following environment variables:
PROXY_USERNAME
PROXY_PASSWORD
1export HTTPS_PROXY=https://your-proxy-url:port2export PROXY_USERNAME=username3export PROXY_PASSWORD=password
Uploading Reports to Evinced Platform
Introduction
Evinced Platform allows you to seamlessly collect, organize, visualize and monitor Evinced accessibility reports in one place. In this section, we will guide you through the key functionalities of the upload methods of the accessibility reports from the Evinced SDK to the Evinced Platform, which was introduced in version 1.3.0. This upload method is fully compatible with the previous versions of the Evinced SDK API, and is disabled by default.
Enable Upload Report to Platform
To enable uploading of accessibility reports to the Evinced Platform,
set the enableUploadToPlatform option to true via
the global setUploadToPlatformConfig method:
1import { setUploadToPlatformConfig } from "@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk";2setUploadToPlatformConfig({ enableUploadToPlatform: true });
You can also use the external config evConfig.json and add the values to be loaded.
Important! The external config has more precedence if both initialization options are used.
1 "uploadToPlatformOptions": {2 "enableUploadToPlatform": true,3 "setUploadToPlatformDefault": false4 }
Note: Using uploadToPlatform: true in method parameters (e.g., evincedService.evAnalyze({ uploadToPlatform: true })) is not sufficient on its own. You must first enable the feature by setting enableUploadToPlatform: true via setUploadToPlatformConfig() or evConfig.json. The method parameter only controls whether a specific report uploads when the feature is already enabled.
Automatic Report Upload
Once the enableUploadToPlatform method is set to true and setUploadToPlatformDefault is true (which is the default),
all generated reports will be automatically uploaded to the Platform immediately upon calling the evStop() or evAnalyze() command.
How it works:
- When
enableUploadToPlatform: trueandsetUploadToPlatformDefault: true (default), upload happens automatically - No additional code is needed - just call
evAnalyze()orevStop()and the report uploads - Upload occurs synchronously as part of the command execution
If you want to change this behavior and control uploads manually, set the setUploadToPlatformDefault feature flag to false.
1setUploadToPlatformConfig({2 enableUploadToPlatform: true,3 setUploadToPlatformDefault: false,4});
If the setUploadToPlatformDefault is disabled, you can still upload
selected reports to the platform.
For that, use the following parameter in the evStop() command:
1await evincedService.evStop({ uploadToPlatform: true });
Or, in the evAnalyze() command:
1await evincedService.evAnalyze({ uploadToPlatform: true });
Test Names
To facilitate report management and be able to distinguish between different reports on the Platform, use the addLabel method to inform the test name and test class.
It’s recommended to do that in the “beforeEach” hook.
1let evincedService;2fixture`Upload to platfrom`.beforeEach(async (t) => {3 evincedService = new EvincedSDK(t);4 evincedService.addLabel({ testName: t.test.name });5});
Labels and Custom Fields
You can attach labels and custom fields to your report to enhance readability and organization in the platform. Labels help you filter, search, and organize reports on the Evinced Platform.
There are two types of labels:
Built-in Labels: Pre-defined labels that can be set using the addLabel method. Available built-in labels include:
testName- The name of the testtestFile- The file path of the testenvironment- The environment where the test runs (e.g., "Development", "Staging", "Production")flow- The test flow identifiergitBranch- The Git branch namegitUserName- The Git user namegitVersion- The Git commit version
Custom Labels: Flexible key-value pairs that can be set using the customLabel method. You can use any custom key-value pairs, including:
- Single values:
{ productVersion: '1.0.0' } - Multiple values (arrays):
{ browsers: ['Chrome', 'Firefox'] } - Special label
unitId: Use this to tag tests for relevant units within your organization
See the following code examples of how to set up labels:
1let evincedService;2fixture`Upload to platform`.beforeEach(async (t) => {3 evincedService = new EvincedSDK(t);45 // Set built-in labels6 evincedService.addLabel({7 testName: t.test.name,8 environment: 'Development',9 gitBranch: 'main'10 });1112 // Set custom labels (including unitId for organizational tagging)13 evincedService.customLabel({14 customParameter: "demo value",15 productVersion: "1.00",16 browsers: ["Chrome 1.00", "Firefox 2.00"],17 SDK: "TestCafe",18 unitId: 'unit-123' // Tag for organizational unit19 });20});
Use of beforeEach and afterEach Hooks
We recommend using the beforeEach and afterEach hooks to control analysis sessions and upload reports to the platform. This way, each test will be uploaded separately with its own report.
In beforeEach hook use evStart() to start Evinced analysis and set any labels
you want for the report to contain when uploading to the platform.
In the afterEach hook call evStop() to stop analysis and upload reports to the platform.
See this code example:
1let evincedService;2fixture`Upload to platfrom`3 .beforeEach(async (t) => {4 evincedService = new EvincedSDK(t);5 evincedService.addLabel({ testName: t.test.name });6 await evincedService.evStart();7 })8 .afterEach(async (t) => {9 await evincedService.evStop({ uploadToPlatform: true });10 });
Putting All of This Together
Here is a complete code snippet of how to perform uploads to the platform on a per-test basis.
1import { setOfflineCredentials, EvincedSDK } from "@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk";2let evincedService;3fixture`Upload to platfrom`4 .before(async (t) => {5 setOfflineCredentials({6 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,7 token: process.env.EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN,8 });9 })10 .beforeEach(async (t) => {11 evincedService = new EvincedSDK(t);12 evincedService.addLabel({ testName: t.test.name });13 evincedService.customLabel({14 customParameter: "demo value",15 productVersion: "1.00",16 SDK: "TestCafe",17 });18 await evincedService.evStart();19 })20 .afterEach(async (t) => {21 await evincedService.evStop({ uploadToPlatform: true });22 });23test("Check upload to platform using evStop", async (t) => {24 await t.navigateTo("https://demo.evinced.com/");25});
Tutorials
You can find fully functional example projects on our GitHub.
Generating a comprehensive accessibility report for your application
In this tutorial, we will enhance our existing JS TestCafe UI test with the Evinced TestCafe JS SDK in order to check our application for accessibility issues. In order to get started you will need the following:
- All of the prerequisites for the Evinced TestCafe JS SDK should be met
- Evinced TestCafe JS SDK should be added to your project
Preface - existing UI test overview
Let’s consider the following basic UI test as our starting point.
1const { fixture } = require("testcafe");2const { ClientFunction } = require("testcafe");34fixture`Evinced Demo site tests`.page`https://demo.evinced.com/`;56test("Demo page. Single page analyze", async (t) => {7 // Example action to verify we are on the correct page8 await t9 .expect(ClientFunction(() => document.title)())10 .eql("Evinced - Demo Page");11});
We wrote this test for a demo travel site called TRVL that has a few known accessibility issues.
The purpose of this test is to check the functionality of the main application screen and ensure a user can successfully select their desired trip. For now, this test is only concerned with the functional testing of the app. However, with the help of the Evinced TestCafe JS SDK, we can also check it for accessibility issues along the way. Let’s go through this process with the following step-by-step instructions.
Step #1 - Importing the Evinced TestCafe JS SDK
In your test file add the following lines to add the Evinced engine to your project.
1const { EvincedSDK } = require("@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk");
Step #2 - Start the Evinced engine
Now that we have everything we need to scan for accessibility issues, let’s start the Evinced engine and set credentials. Let's use the offline setting for this example. Since we are going to use it scan throughout our test, the best place for its initialization will be our beforeEach method.
1const { fixture } = require("testcafe");2const { EvincedSDK } = require("@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk");34fixture`Evinced Demo site tests`.page`https://demo.evinced.com/`5 .before(async (ctx) => {6 // Set offline credentials7 setOfflineCredentials({8 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,9 token: process.env.EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN,10 });11 })12 .beforeEach(async (t) => {13 // Initialize Evinced SDK14 evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);15 // Start the Evinced engine16 await evinced.evStart();17 });1819test("Demo page. Single page analyze", async (t) => {20 // Example action to verify we are on the correct page21 await t22 .expect(ClientFunction(() => document.title)())23 .eql("Evinced - Demo Page");24});
Step #3 - Stop the Evinced engine and create reports
As our test was executed we collected a lot of accessibility information. We can now perform accessibility assertions at the end of our test suite. Referring back again to our UI test the best place for this assertion will be the method that gets invoked last - after. To stop the Evinced engine and generate the actual object representation of your accessibility report simply call the evStop() method.
1const { fixture } = require("testcafe");2const { EvincedSDK } = require("@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk");34fixture`Evinced Demo site tests`.page`https://demo.evinced.com/`5 .before(async (ctx) => {6 // Set offline credentials7 setOfflineCredentials({8 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,9 token: process.env.EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN,10 });11 })12 .beforeEach(async (t) => {13 // Initialize Evinced SDK14 evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);15 // Start the Evinced engine16 await evinced.evStart();17 })18 .afterEach(async (t) => {19 const issues = await evinced.evStop();20 });2122test("Demo page. Single page analyze", async (t) => {23 // Example action to verify we are on the correct page24 await t25 .expect(ClientFunction(() => document.title)())26 .eql("Evinced - Demo Page");27});
For the sake of simplicity of this tutorial let’s simply assume that our application is accessible as long as it has no accessibility issues found. Thus, if we have at least one accessibility issue detected - we want our tests to be failed. Let’s add the corresponding assertion to our after method. For more information regarding reports as well as the Report object itself, please see our detailed Web Reports page.
1...2 .afterEach(async (t) => {3 const issues = await evinced.evStop();4 await t.expect(issues.length).eql(0);5 });6...
You are now set to run the test and ensure the accessibility of your application! So, go ahead and run it via your IDE or any other tooling you use for JavaScript development.
Fail the test if critical issues are found
Here you can see a way of failing your test if critical accessibility issues are found using the TestCafe JS SDK.
Using evAnalyze:
1const issues = await evinced.evAnalyze();23const criticalIssues = issues.filter((issue) => issue.severity.name === 'Critical');4await t.expect(criticalIssues.length).eql(0);
Using evStart/evStop:
1await evinced.evStart();2const issues = await evinced.evStop();34const criticalIssues = issues.filter((issue) => issue.severity.name === 'Critical');5await t.expect(criticalIssues.length).eql(0);
The criticalIssues array will contain all the critical issues found during the scan. If the array is not empty, the test will fail on the assertion.
Complete Test Suite Integration
To integrate the Evinced TestCafe SDK into your test suite with global hooks, you can use TestCafe's support for testRun, fixture, and test hooks. These hooks ensure that the Evinced SDK is properly initialized and managed across your test suite, reducing setup effort and improving consistency.
Create a .testcaferc.js configuration file to reuse the same TestCafe settings across multiple test runs.
This approach centralizes your test configuration and simplifies your test execution process. Below is an example of a .testcaferc.js file:
1const { setOfflineCredentials, EvincedSDK } = require("@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk");23module.exports = {4 hooks: {5 // Each unique launch of TestCafe constitutes a single test run.6 // Test run hooks cannot access the browser.7 testRun: {8 before: async () => {9 console.log('Global testRun before hook');10 },11 after: async () => {12 console.log('Global testRun after hook');13 },14 },15 // Global fixture hooks run before/after each of the fixtures in your test suite.16 // Fixture hooks cannot access the browser.17 fixture: {18 before: async () => {19 console.log('Global Fixture before hook');20 setOfflineCredentials({21 serviceId: process.env.AUTH_SERVICE_ID,22 token: process.env.AUTH_TOKEN,23 });24 },25 after: async () => {26 console.log('Global Fixture after hook');27 },28 },29 // Global test hooks run before/after each of the tests in your entire test suite.30 // Hooks that run before and after tests can access the browser.31 test: {32 before: async t => {33 console.log('Global Test before hook');34 t.ctx.evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);35 await t.ctx.evinced.evStart();36 },37 after: async t => {38 console.log('Global Test after hook');3940 const issues = await t.ctx.evinced.evStop();41 // Note that if you have multiple tests, this will overwrite the file so consider using a dynamic file name42 await t.ctx.evinced.evSaveFile('issues', 'html', 'evincedTest.html');4344 // Dynamic test naming45 const testName = t.testRun.test.name.replace(/\s+/g, '_');46 await t.ctx.evinced.evSaveFile(issues, 'html', `${testName}.html`);47 },48 },49 },50};51
Support
Please feel free to reach out to support@evinced.com with any questions.
FAQ
- Can I configure which validations to run?
Yes, see the Configuration section for details on how to configure Axe validations to your needs.
- Can I run tests with Evinced using cloud-based services like Sauce Labs, Perfecto, or BrowserStack?
Yes, we have tested the Evinced SDK on many of these types of cloud-based services and expect no issues.
- Why does test execution slow down significantly or get stuck when I run tests concurrently?
This can happen if the Evinced object is shared between tests, which may cause race conditions. To avoid this, isolate Evinced for every test by using the Context object provided by TestCafe. Context can be accessed using t.ctx in TestCafe tests.
1const { fixture } = require("testcafe");2const { EvincedSDK } = require("@evinced/js-testcafe-sdk");34fixture`Evinced Demo site tests`.page`https://demo.evinced.com/`5 .before(async (ctx) => {6 // Set offline credentials7 setOfflineCredentials({8 serviceId: process.env.EVINCED_SERVICE_ID,9 token: process.env.EVINCED_AUTH_TOKEN,10 });11 })12 .beforeEach(async (t) => {13 // Initialize Evinced SDK and save to context14 t.ctx.evinced = new EvincedSDK(t);15 // Start the Evinced engine16 await t.ctx.evinced.evStart();17 })18 .afterEach(async (t) => {19 const issues = await t.ctx.evinced.evStop();20 });2122test("Demo page. Single page analyze", async (t) => {23 // Example action to verify we are on the correct page24 await t25 .expect(ClientFunction(() => document.title)())26 .eql("Evinced - Demo Page");27});